Unveiling the Power of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) in Modern Cybersecurity
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, traditional perimeter-based security models are proving inadequate against sophisticated threats. As organizations grapple with the increasing complexity of their networks and the rise in cyberattacks, the Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) emerges as a paradigm shift in cybersecurity strategy. This article delves into the principles, implementation, and benefits of Zero Trust, offering a comprehensive understanding of how it can fortify organizations against modern cyber threats.
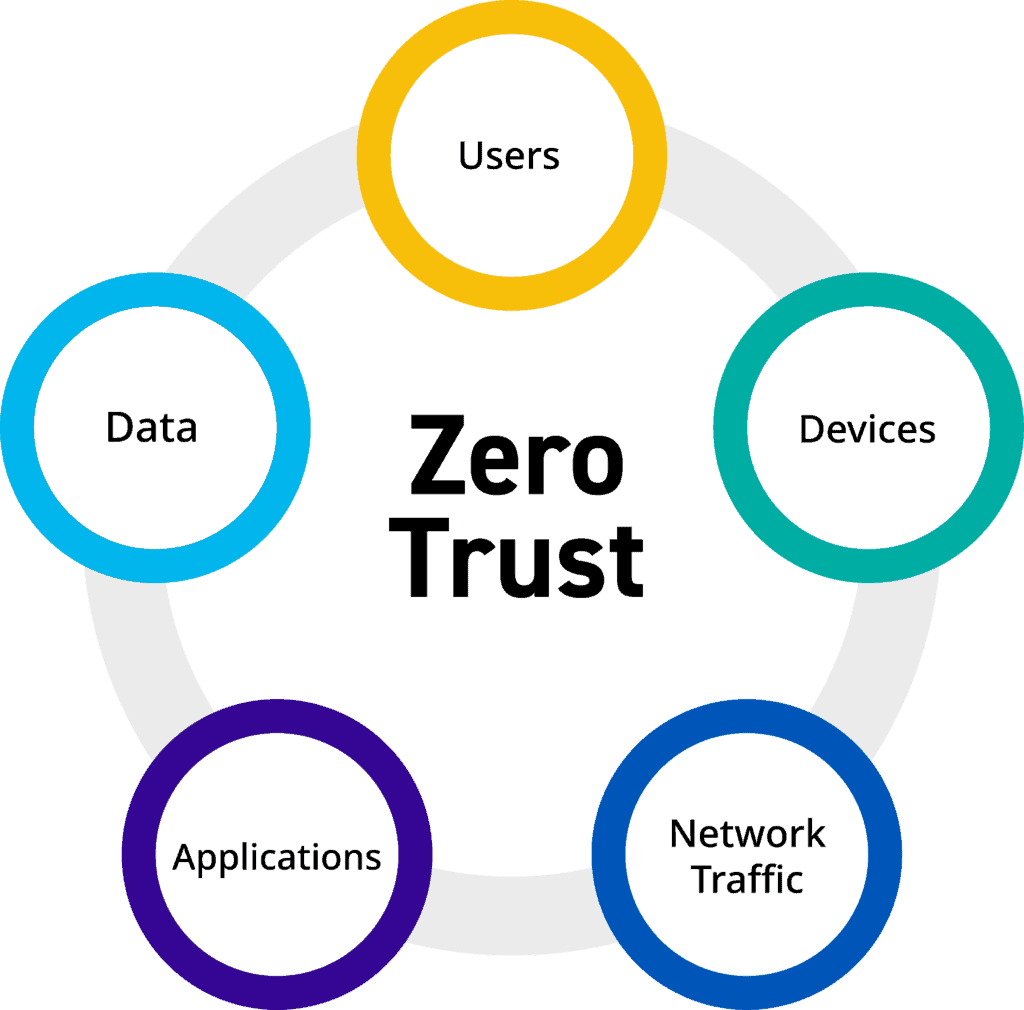
Understanding Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust challenges the traditional “trust but verify” approach by assuming that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. Instead, it advocates for continuous verification of the security posture of every user, device, or system attempting to connect to the network. The foundation of Zero Trust lies in the principle of “never trust, always verify.”
Key Components of Zero Trust:
- Micro-Segmentation: Break down the network into smaller, isolated segments, ensuring that even if one segment is compromised, the rest remain secure. This limits lateral movement for attackers within the network.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Emphasize the importance of strong identity verification before granting access. Implement multifactor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access principles to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- Continuous Monitoring: Employ real-time monitoring and analytics to assess the security posture of users, devices, and applications. Any deviation from the baseline triggers an immediate response.
- Encryption: Apply encryption throughout the network to protect data in transit and at rest. This ensures that even if a malicious actor gains access to the network, the data remains unintelligible without the appropriate decryption keys.
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture
- Inventory and Classification: Begin by creating an inventory of all assets and classifying them based on their criticality and sensitivity. This enables organizations to prioritize protection efforts.
- Define Trust Zones: Identify trust zones within the network, grouping assets with similar security requirements. Implement micro-segmentation to create barriers between these zones.
- Zero Trust Policies: Develop and enforce access policies based on the principle of least privilege. Regularly review and update these policies to reflect changes in the network and organizational structure.
- Continuous Authentication and Authorization: Implement tools and solutions for continuous authentication and authorization, ensuring that users and devices are re-authenticated regularly during their session.
Benefits of Zero Trust Architecture:
- Reduced Attack Surface: By implementing micro-segmentation and least privilege access, Zero Trust significantly reduces the attack surface, limiting the potential impact of a security breach.
- Improved Incident Response: Continuous monitoring and real-time analytics enable organizations to detect and respond to security incidents promptly, minimizing the time attackers have to operate within the network.
- Enhanced Compliance: Zero Trust aligns with many regulatory requirements by enforcing strong access controls and data protection measures, facilitating compliance with data protection laws.
- Adaptability to Dynamic Environments: In today’s dynamic business environment, Zero Trust accommodates changes seamlessly, allowing organizations to scale and adapt without compromising security.
Conclusion: Zero Trust Architecture represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, acknowledging the persistent threat landscape and the need for a proactive, continuous approach to security. Organizations that embrace Zero Trust not only fortify their defenses against evolving threats but also create a resilient and adaptive security posture. As cybersecurity continues to evolve, Zero Trust stands as a cornerstone for building a secure and trustworthy digital future.
You think you have a story worth everyone’s time? SUBMIT A STORY and we will publish it.
Share this content:



Post Comment